LDX Solutions has been cleaning the air with custom-engineered solutions at industrial sites since 1937, and we provide everything needed for pre-cleaning a gas stream prior to treatment in a CO2 scrubber.
Carbon Capture
Carbon Capture refers to the process of capturing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions from industrial sources or the atmosphere, then transporting and storing them to prevent their release into the atmosphere. This is a key technology aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
In Carbon Capture and Sequestration/Storage (CCS) the CO₂ is pumped deep underground in geological formations, effectively preventing it from entering the atmosphere and contributing to climate change.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration/Storage (CCUS) takes this a step further by purifying the CO2 gas and finding practical applications for the captured carbon.
Carbo Capture can have an effect on all industries
1. Fossil Fuel Combustion (Energy Sector):
The energy sector, including power plants and refineries, is the largest source of CO₂ emissions globally. It uses fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity and heat, producing a significant amount of CO₂ as a byproduct.
2. Cement and Concrete Production:
Cement manufacturing is a major contributor to CO₂ emissions. The chemical process of converting limestone to clinker releases CO₂, and the energy-intensive heating processes used in production also burn large amounts of fossil fuels.
3. Steel and Iron Production:
The steel industry uses carbon-intensive processes such as the blast furnace method, where coal is burned to convert iron ore into steel, releasing substantial

Uses of CO2
Some Common Uses of CO2 Include:
Chemical Industry
CO₂ is used in the production of chemicals like urea, which is used in fertilizers. The chemical sector also uses CO₂ in processes such as the production of methanol, plastics, and synthetic fuels.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
The oil and gas industry uses large quantities of CO₂ for Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR), where CO₂ is injected into oil reservoirs to increase the amount of crude oil that can be extracted.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage sector, CO₂ is used for carbonation in drinks, preservation, and packaging. It also helps in the freezing and cooling of food products.

Pharmaceutical and Medical Uses
CO₂ is used in supercritical fluid extraction for drug formulation, as well as for sterilization in the pharmaceutical industry.
Agriculture (Greenhouses)
CO₂ is used to stimulate plant growth in greenhouse environments. Farmers introduce CO₂ into greenhouses to enhance photosynthesis and increase crop yields.
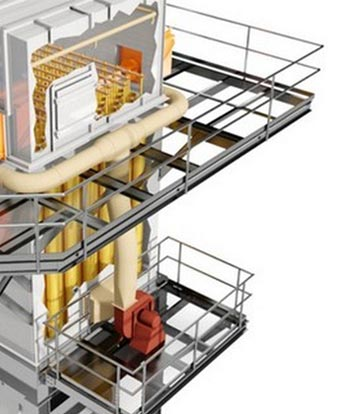
Clean Gas is Necessary for CO2 Scrubbers – The Wet ESP
The most widely applied CO2 scrubbing technology uses an aqueous monoethanolamine (MEA) solution to absorb dilute CO2 and render it into a concentrated form after desorption. While the MEA CO2 scrubbing process is proven, it is also costly to operate, and one of the main OPEX factors is solvent loss from the presence of contaminants in the inlet gas stream.
Reported experience also shows that the cleanliness of the inlet gas stream is essential in minimizing maintenance costs. Solid particulate matter in the incoming gas stream can foul equipment such as the heat exchangers in the scrubbing system.

Wet ESP Removing all contaminants is essential for Carbon Capture
Wet ESPs have several characteristics that make them well-suited for precleaning a gas stream prior to treatment in a CO2 scrubber. Because they operate in cooled, saturated conditions, they can capture condensable particulate such as acid mist and heavy organics. In addition, they are not sensitive to the chemical makeup of the collected particles.
Wet ESP – Wet Electrostatic Precipitator